| SCOP classification |
| a.4.5.69 C: All alpha proteins F: DNA/RNA-binding 3-helical bundle S: "Winged helix" DNA-binding domain F: HxlR-like |
| a.45.1.1 C: All alpha proteins F: Glutathione S-transferase (GST), C-terminal domain S: Glutathione S-transferase (GST), C-terminal domain F: Glutathione S-transferase (GST), C-terminal domain |
| a.166.1.1 C: All alpha proteins F: RuBisCo LSMT C-terminal, substrate-binding domain S: RuBisCo LSMT C-terminal, substrate-binding domain F: RuBisCo LSMT C-terminal, substrate-binding domain |
| a.211.1.2 C: All alpha proteins F: HD-domain/PDEase-like S: HD-domain/PDEase-like F: PDEase |
| a.138.1.3 C: All alpha proteins F: Multiheme cytochromes S: Multiheme cytochromes F: Di-heme elbow motif |
| b.43.3.1 C: All alpha proteins F: R1 subunit of ribonucleotide reductase, N-terminal domain S: R1 subunit of ribonucleotide reductase, N-terminal F: R1 subunit of ribonucleotide reductase, N-terminal |
| b.70.3.1 C: All beta proteins F: Immunoglobulin-like beta-sandwich S: Immunoglobulin F: I set domains |
| c.2.1.5 C: Alpha and beta proteins (a/b) F: NAD(P)-binding Rossmann-fold domains S: NAD(P)-binding Rossmann-fold domains F: LDH N-terminal domain-like |
| c.44.1.1 C: Alpha and beta proteins (a/b) F: Phosphotyrosine protein phosphatases I-like S: Phosphotyrosine protein phosphatases I F: Low-molecular-weight phosphotyrosine protein |
| c.69.1.7 C: Alpha and beta proteins (a/b) F: alpha/beta-Hydrolases S: alpha/beta-Hydrolases F: Proline iminopeptidase-like |
| d.58.7.1 C: Alpha and beta proteins (a+b) F: Ferredoxin-like S: RNA-binding domain, RBD F: Canonical RBD |
| d.240.1.1 C: Alpha and beta proteins (a+b) F: Lesion bypass DNA polymerase (Y-family), little finger S: Lesion bypass DNA polymerase (Y-family), little F: Lesion bypass DNA polymerase (Y-family), little finger |
| Gene Ontology |
| Molecular Function |
| Cellular Component |
| Other Databases |
| CSU |
| PDB lite |
| DSSP |
| PDB ID | 2ea1 |
| Chain | A |
| N | 245 |
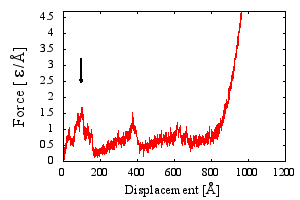
| Fmax [ε/Å] | 1.62 |
| Fmax [pN] | 178.2 |
| ΔFmax [ε/Å] | 0.08 |
| Dmax [Å] | 110.23 |
| Lmax [Å] | 97 |
| λ | 0.08 |
| nSS | 0 |
For help click on values in the Table.
Latest estimate of force unit, ε/Å is 110+/-30 [pN]. For details see our paper.
Chain
Opis Chain
Opis Chain
xN
Number of amino-acids in the structure
Number of amino-acids in the structure
xFmax
In the force-displacement curve the height of a highest force peak. Final stage of protein stretching resulting in hooke`an linear force growth is excluded. If a curve has no apparent peaks, the Fmax is arbitrarily set to 0.
In the force-displacement curve the height of a highest force peak. Final stage of protein stretching resulting in hooke`an linear force growth is excluded. If a curve has no apparent peaks, the Fmax is arbitrarily set to 0.
xFmax
Estimated value of Fmax in pN
Estimated value of Fmax in pN
xΔFmax
Standard deviation of Fmax across saveral trajectories
Standard deviation of Fmax across saveral trajectories
xLmax
End-to-end at which the force rises to Fmax.
End-to-end at which the force rises to Fmax.
xDmax
Tip displacement at which the force rises to Fmax.
Tip displacement at which the force rises to Fmax.
xLambda
λ=(Lmax - Ln)/(Lf - Ln) where Ln is the native end-to-end distance in the structure,
Lf denominates end-to-end distance at full extension. lambda varies between 0 and 1. Small values of lambda indicate occurance of the maximum force at the beginning of the pulling process. Note, that the disulphide bridges may not allow for the full extension.
nSS: the number of disulphide bridges in protein structure
λ=(Lmax - Ln)/(Lf - Ln) where Ln is the native end-to-end distance in the structure,
Lf denominates end-to-end distance at full extension. lambda varies between 0 and 1. Small values of lambda indicate occurance of the maximum force at the beginning of the pulling process. Note, that the disulphide bridges may not allow for the full extension.
nSS: the number of disulphide bridges in protein structure
xnSS
The number of disulphide bridges in protein structure.
The number of disulphide bridges in protein structure.